AI (Artificial Intelligence)
AI is a collective term for all technologies and systems that can independently analyze data, recognize patterns, make predictions, and take decisions—tasks that previously required human judgment. Using so-called machine learning and deep learning techniques, computers learn from large amounts of data, allowing them to continuously adapt and improve without every step having to be programmed manually.
With machine learning techniques, computers learn from data based on pre-labeled examples and human guidance (such as recognizing spam from labeled emails).
With deep learning, the computer itself learns to identify relevant patterns and features from large datasets, without a human having to specify the features beforehand—think of facial recognition or speech recognition using neural networks.
Where does it come from?
The term Artificial Intelligence (“kunstmatige intelligentie”) was introduced in 1956 during a research conference at Dartmouth (USA). There, John McCarthy proposed to “make machines intelligent” by teaching them to reason like humans. The story goes that the researchers thought they could make huge strides in one summer. In reality, it turned out to be much more complex: real progress only came decades later, when sufficient data, computing power, and advanced algorithms became available.
- 1980–1990: first breakthrough with expert systems and the rise of more accessible machine learning techniques.
- 2000–2010: internet and digitization generated massive amounts of data, but computing power was still limited.
- After 2010: real acceleration with deep learning and powerful GPUs, enabling practical applications such as image and speech recognition.
- From 2020: breakthroughs with large language models (such as GPT-3, GPT-4) and generative AI that became accessible to a broad public.
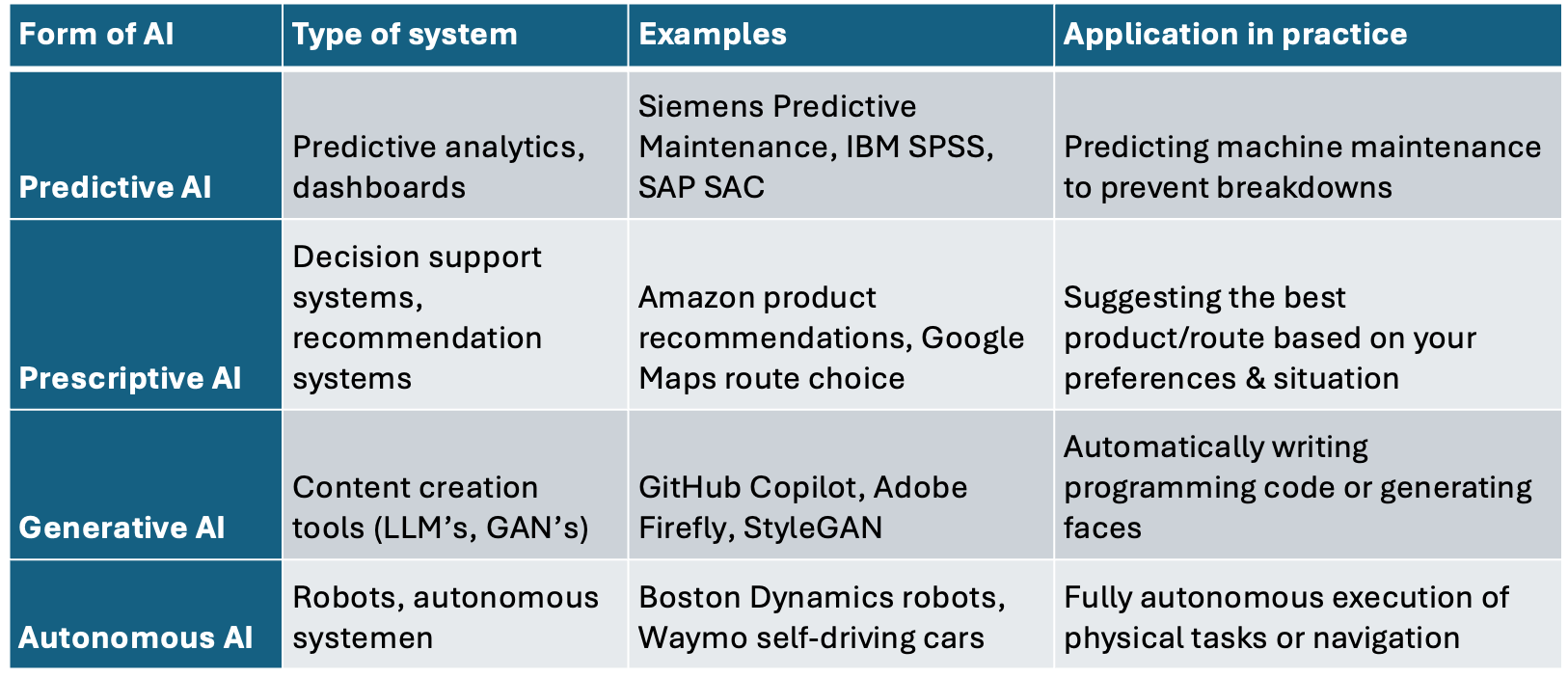
Forms of AI
AI takes different forms, depending on the purpose for which it is used. Some applications are predictive, others advisory or creative, and yet others take fully autonomous decisions.
Examples of AI in practice
- The Netflix recommendation algorithm: it continuously learns from the viewing behavior of millions of users and keeps adapting itself, so over time it can provide better and more personalized viewing suggestions—without each recommendation being manually preprogrammed.
- AI in self-driving cars: these vehicles continuously analyze data from sensors and cameras, recognize patterns in traffic, predict the actions of other road users, and make autonomous decisions—such as braking, steering, or changing lanes—without direct human intervention.
AI in Media: Opportunities and Challenges
AI now plays a major role in the media sector. It is used for more efficient content creation and a more personalized media experience. At the same time, this development raises challenges around transparency, ethics, and trust, as AI increasingly takes over editorial tasks. The challenge for everyone in the sector: keep innovating, but don’t lose sight of the human touch.

